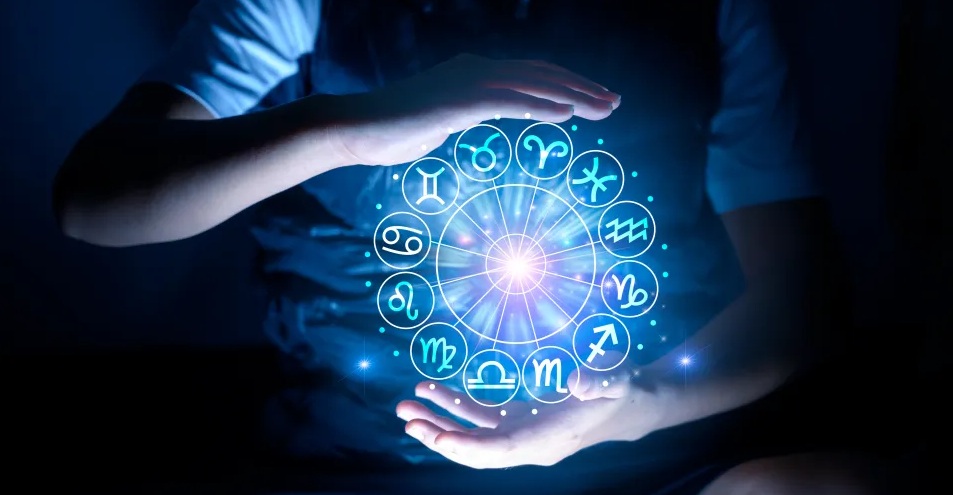
Astrology is a set of divinatory practices that proposes a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events on Earth, particularly human affairs and personality. It’s based on the idea that the positions and movements of celestial objects like the Sun, Moon, and planets at specific moments (like a person’s birth) can influence or indicate trends in individuals, groups, or nations.
Key aspects of astrology include:
- Horoscopes: A central element of Western astrology is the creation of a “birth chart” or “natal chart,” which is a map of the sky at the exact moment and location of a person’s birth. This chart depicts the positions of planets within specific zodiac signs (twelve divisions of the sky) and astrological “houses” (twelve divisions of the sky based on earthly rotation), as well as the geometric angles (aspects) between these celestial bodies.
- Zodiac Signs: The twelve zodiac signs (Aries, Taurus, Gemini, etc.) are based on constellations that the Sun appears to pass through at different times of the year. Each sign is associated with particular personality traits and characteristics.
- Planetary Influences: Different planets are believed to exert specific influences. For example, Venus might be associated with love and relationships, while Mercury could relate to communication.
- Divination and Prediction: Historically, astrology has been used for various forms of divination, from predicting natural disasters and political events to forecasting individual destinies and providing guidance for decision-making. While some modern approaches focus on self-reflection and personal growth, the predictive aspect remains a common perception.
History of Astrology:
Astrology has ancient roots, with its earliest organized systems emerging in Mesopotamia (Babylonia) around the 2nd millennium BCE. The Babylonians developed the zodiac and linked constellations to their agricultural calendar and celestial omens. Egyptian and Greek traditions later influenced its development, with Hellenistic astrology, in particular, systematizing horoscopic astrology.
Throughout much of history, astrology and astronomy were intertwined, and many prominent astronomers were also astrologers. However, with the Scientific Revolution and the development of modern science, particularly after the 17th century, astronomy diverged as a scientific discipline based on empirical observation and falsifiable theories, while astrology became largely regarded as a pseudoscience due to its lack of testable and verifiable results.
Astrology vs. Astronomy:
It’s important to distinguish between astrology and astronomy.
- Astronomy is the scientific study of celestial objects, the universe, and the physical laws governing them.
- Astrology, on the other hand, is a belief system or divinatory practice that posits a connection between celestial positions and earthly events, and is not supported by scientific evidence.